Sandblasting
Our CNC‑aligned abrasive blasting service uses high‑velocity compressed air to propel precise media—such as glass beads, aluminum oxide, or steel grit—against machined components.
NDA available upon request before quoting.
Sandblasting Process and Its Applications

Sandblasting, also known as abrasive blasting, is a surface treatment process that uses pressurized air to propel abrasive media onto a workpiece. In the specific case of bead blasting, fine, spherical media (such as glass beads) are employed to uniformly impact the surface. This method effectively removes surface contaminants and creates a consistent matte finish, all while preserving the underlying material’s integrity. The process is particularly beneficial when a uniform surface profile is required for subsequent finishing steps, such as painting or coating.
Key Applications:
Automotive: Prepares metal components for coatings, ensuring optimal adhesion and a uniform, aesthetically pleasing finish.
Aerospace: Cleans and textures structural parts, providing a consistent surface profile essential for high-performance applications.
Construction: Enhances surface preparation for various substrates, promoting better adhesion of protective coatings and finishes.
Furniture: Achieves a refined matte finish on decorative elements while maintaining the material’s durability and strength.
Surface properties
| Tolerances | Premium appearance availability | Sharp edges and burrs | Applicable |
| Met after surface finish | yes | Removed | Metals &Plastics |
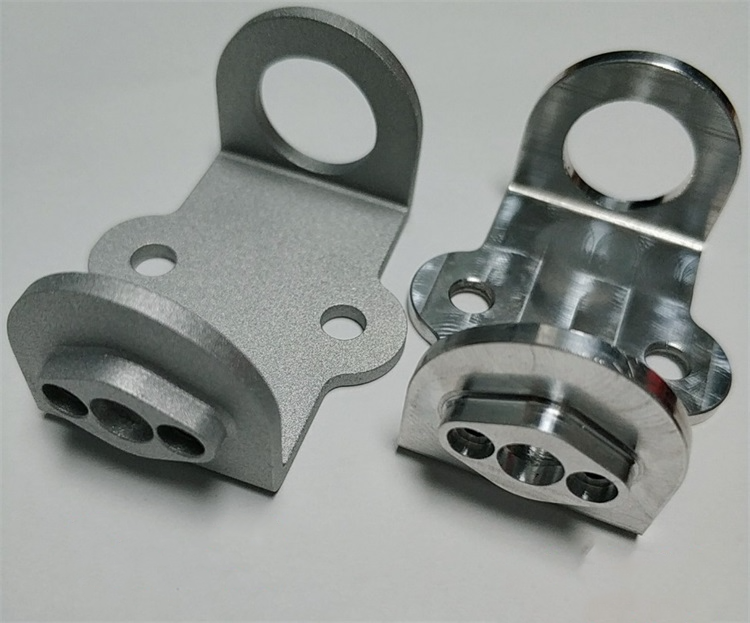

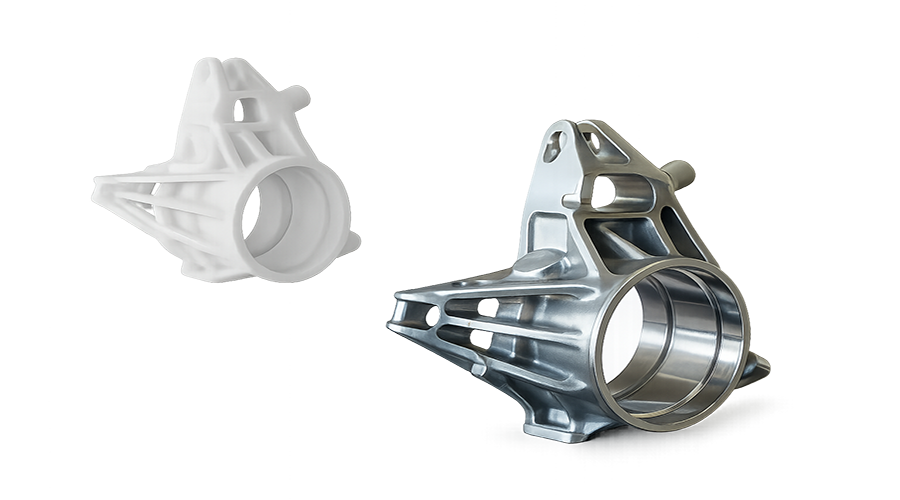
compares two parts with different surface treatments
Sandblasting effect samples



What kind of blasting media is employed in your process?
mazaro’s sand blasting services utilize tailored media—including silica sand, aluminum oxide, steel grit, and glass beads—to precisely control surface preparation. Silica sand is ideal for general cleaning, aluminum oxide for aggressive abrasion, steel grit for removing coatings and rust, and glass beads for gentle cleaning of delicate surfaces.
Which blasting media is effective at removing rust?
Aluminum oxide is ideal for removing light to moderate rust with aggressive abrasion yet minimal substrate damage, while steel grit’s angular shape and hardness make it suitable for heavy rust and corrosion removal, effectively cleaning and preparing surfaces for further treatment.
Is there a risk of warping or damaging parts during sandblasting?
In sandblasting operations, there is an inherent risk of part distortion or damage, especially when processing thin or delicate materials with high-pressure equipment or aggressive abrasive media. The kinetic energy delivered by the abrasive particles can exceed the structural tolerances of sensitive components, resulting in warping, distortion, or surface degradation.
Is it possible to blast objects made from fiberglass or plastic?
Yes, it is possible to blast objects made from fiberglass or plastic. However, due to the softer nature of these materials, conventional abrasives like sand or aluminum oxide may cause damage or deformation. Instead, using gentler media—such as plastic beads, walnut shells, or baking soda—provides controlled, low-impact abrasion that effectively cleans or prepares the surface without compromising its integrity.
Should a protective coating be applied after the blasting process?
After the blasting process, it is essential to apply a protective coating to safeguard parts against oxidation and corrosion. While blasting effectively removes contaminants and primes the surface for further treatment, it also exposes the substrate to environmental factors that may accelerate deterioration. Applying a protective finish—such as specialized paints or primers—seals the surface, creating an additional barrier against moisture, chemicals, and other corrosive agents, thereby enhancing the component’s durability and longevity.
